如果要在redis查找遍历key,keys命令会阻塞,是不能用的,这时就要用scan命令。
scan命令支持传入cursor、match pattern、count、type(6.0新增type),根据游标,返回count数量的符合条件的key,以及新游标。注意这个count只是一个期望值,看源码就知道为什么不是确切值。
db是由dict组成的,set、hash、ziplist也是有dict类型的,dict发生扩容和缩容的话,如果按自然数的方法去遍历,扩容会重复遍历,缩容会遗漏遍历。
假设dict稳定状态下,dict size从8变成16,刚访问过index为3的桶,接下来就应该遍历4-15桶,由于原先0-3号的桶的key有一部分挪到8-11中(+8),后面就会重复遍历到。
假设dict size从8变成4,刚访问过index为3的桶,那么接下来就是遍历结束了,这样原先4-7号的桶就会漏掉(-4)。
如果在扩容缩容情况下,需要遍历两条数组,同样会遇到上面的问题。
看看redis是怎么解决的。
redis不采用自然数顺序遍历,而是采用高位顺序遍历,也就是对游标前进的方式是酱紫的:用对应数组的掩码将游标的值截断(准确地说不是截断,可以先用截断理解) —> 左右翻转 -> 自增 -> 左右翻转回来。
这个算法的原理是,数组扩容是*2,那么每次扩容,旧数组的元素哈希值& new_mask得到下标,要么在原来的桶,要么是原来桶的index*2,具体表现为最高位分别是0和1。那么从高位起开始遍历的话,如果去掉最高位,其实遍历的顺序和旧数组是一样的。
举个例子,
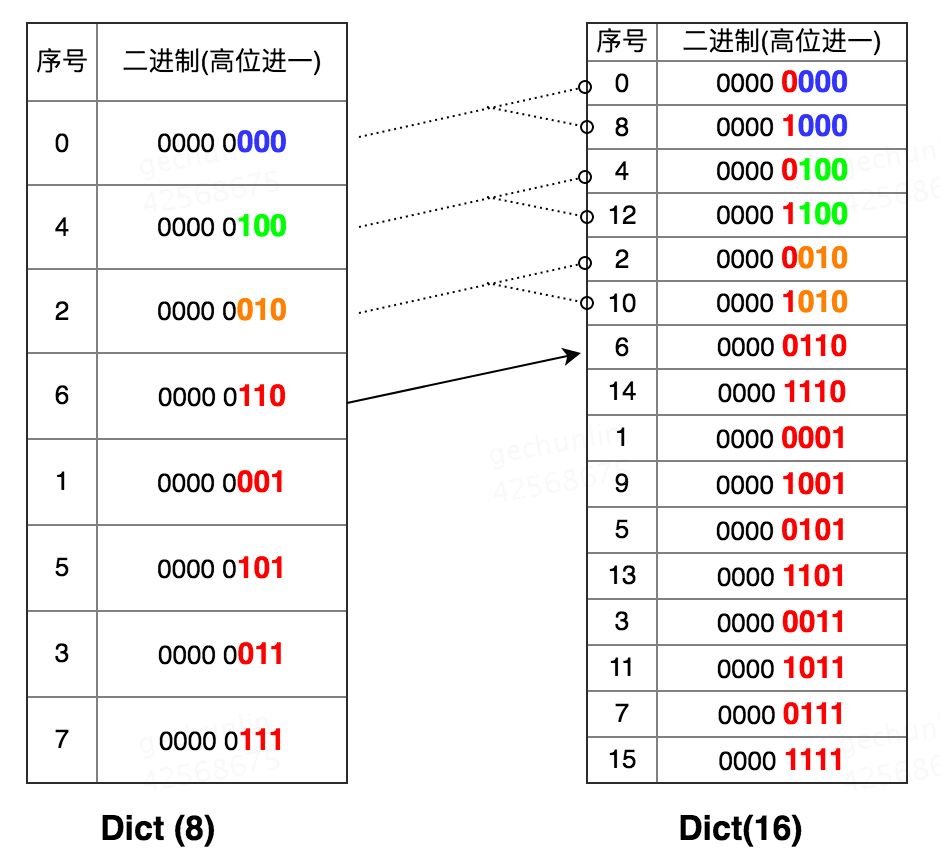 原来的顺序是
原来的顺序是
000
100
010
110
那么扩容后,顺序是
(0)000
(1)000
(0)100
(1)100
(0)010
(1)010
(0)110
(1)100
括号里就是最高位,去掉最高位,和原来的数组是一致的。
遍历实现
代码基于6.0,主要分为两部分,一部分是dict非rehash状态,一部分是rehash状态。
// 这个函数将游标v的元素放到privdata,并用算法推进cursor,
unsigned long dictScan(dict *d,
unsigned long v,
dictScanFunction *fn,
dictScanBucketFunction* bucketfn,
void *privdata)
{
dictht *t0, *t1;
const dictEntry *de, *next;
unsigned long m0, m1;
if (dictSize(d) == 0) return 0;
/* Having a safe iterator means no rehashing can happen, see _dictRehashStep.
* This is needed in case the scan callback tries to do dictFind or alike. */
d->iterators++;
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) {
t0 = &(d->ht[0]);
m0 = t0->sizemask;
/* Emit entries at cursor */
if (bucketfn) bucketfn(privdata, &t0->table[v & m0]);
de = t0->table[v & m0];
while (de) {
next = de->next;
fn(privdata, de);
de = next;
}
/* Set unmasked bits so incrementing the reversed cursor
* operates on the masked bits */
v |= ~m0;
/* Increment the reverse cursor */
v = rev(v);
v++;
v = rev(v);
} else {
t0 = &d->ht[0];
t1 = &d->ht[1];
/* Make sure t0 is the smaller and t1 is the bigger table */
if (t0->size > t1->size) {
t0 = &d->ht[1];
t1 = &d->ht[0];
}
m0 = t0->sizemask;
m1 = t1->sizemask;
/* Emit entries at cursor */
if (bucketfn) bucketfn(privdata, &t0->table[v & m0]);
de = t0->table[v & m0];
while (de) {
next = de->next;
fn(privdata, de);
de = next;
}
/* Iterate over indices in larger table that are the expansion
* of the index pointed to by the cursor in the smaller table */
do {
/* Emit entries at cursor */
if (bucketfn) bucketfn(privdata, &t1->table[v & m1]);
de = t1->table[v & m1];
while (de) {
next = de->next;
fn(privdata, de);
de = next;
}
// 这里曾经有个bug,参考下面美团链接
/* Increment the reverse cursor not covered by the smaller mask.*/
v |= ~m1;
v = rev(v);
v++;
v = rev(v);
// 这个(m0 ^ m1)就是前面说到的高位,我认为这个循环只会执行两次,小数组的一个桶下标对应大数组的两个桶下标
/* Continue while bits covered by mask difference is non-zero */
} while (v & (m0 ^ m1));
}
/* undo the ++ at the top */
d->iterators--;
return v;
}
在非rehash状态,用掩码定位计算cursor对应的桶,用一个循环取出桶下所有entry。
在rehash状态,不用区分是扩容还是缩容,只要需要确定大小数组,循环取出小数组的桶的entry,对于大数组,遍历两个桶的所有entry,并推进cursor
游标推进
cursor推进的算法是
// 这里将非掩码部分置1,如上面说的并非截断
v |= ~m1;
// 翻转
v = rev(v);
// 自增
v++;
// 翻转回来
v = rev(v);
rev函数
/* Function to reverse bits. Algorithm from:
* http://graphics.stanford.edu/~seander/bithacks.html#ReverseParallel */
static unsigned long rev(unsigned long v) {
unsigned long s = CHAR_BIT * sizeof(v); // bit size; must be power of 2
unsigned long mask = ~0UL;
while ((s >>= 1) > 0) {
mask ^= (mask << s);
v = ((v >> s) & mask) | ((v << s) & ~mask);
}
return v;
}
大意是,unsigned long是32位,即把前16位和后16位交换,然后16位里,前8位和后8位交换。。。以此类推,总共5次。
想吐槽这个老哥不是不屑于这种位运算魔法吗 = =
scanGenericCommand
这个方法是scan命令的实现,源代码比较长,注释写的很详细,大约有四步: Step 1: Parse options. 这一步是把参数校验 Step 2: Iterate the collection. 这一步是提取出目标的dict,调用前面的遍历方法。 Step 3: Filter elements. 这一步是根据match过滤或根据type过滤。 Step 4: Reply to the client. 回复客户端
主要看第二步
/* Step 2: Iterate the collection.
*
* Note that if the object is encoded with a ziplist, intset, or any other
* representation that is not a hash table, we are sure that it is also
* composed of a small number of elements. So to avoid taking state we
* just return everything inside the object in a single call, setting the
* cursor to zero to signal the end of the iteration. */
/* Handle the case of a hash table. */
ht = NULL;
if (o == NULL) {
ht = c->db->dict;
} else if (o->type == OBJ_SET && o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {
ht = o->ptr;
} else if (o->type == OBJ_HASH && o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {
ht = o->ptr;
count *= 2; /* We return key / value for this type. */
} else if (o->type == OBJ_ZSET && o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST) {
zset *zs = o->ptr;
ht = zs->dict;
count *= 2; /* We return key / value for this type. */
}
if (ht) {
void *privdata[2];
/* We set the max number of iterations to ten times the specified
* COUNT, so if the hash table is in a pathological state (very
* sparsely populated) we avoid to block too much time at the cost
* of returning no or very few elements. */
long maxiterations = count*10;
/* We pass two pointers to the callback: the list to which it will
* add new elements, and the object containing the dictionary so that
* it is possible to fetch more data in a type-dependent way. */
privdata[0] = keys;
privdata[1] = o;
do {
cursor = dictScan(ht, cursor, scanCallback, NULL, privdata);
} while (cursor &&
maxiterations-- &&
listLength(keys) < (unsigned long)count);
} else if (o->type == OBJ_SET) {
int pos = 0;
int64_t ll;
while(intsetGet(o->ptr,pos++,&ll))
listAddNodeTail(keys,createStringObjectFromLongLong(ll));
cursor = 0;
} else if (o->type == OBJ_HASH || o->type == OBJ_ZSET) {
unsigned char *p = ziplistIndex(o->ptr,0);
unsigned char *vstr;
unsigned int vlen;
long long vll;
while(p) {
ziplistGet(p,&vstr,&vlen,&vll);
listAddNodeTail(keys,
(vstr != NULL) ? createStringObject((char*)vstr,vlen) :
createStringObjectFromLongLong(vll));
p = ziplistNext(o->ptr,p);
}
cursor = 0;
} else {
serverPanic("Not handled encoding in SCAN.");
}
注意遍历停止的条件是cursor && maxiterations > 0 && listlength(keys) < count,
如果需要返回key/value,count *= 2, maxiterations = count * 10;
结合后面的过滤,所以说返回结果的长度不是严格按照我们传入的count的值,有可能超了一丢丢,有可能遍历了10倍count数量的桶没几个元素,也有可能找到很多被过滤了一大堆。
还有一件事,第二步,如果scan目标是集合,且集合数量比较少,没用dict实现,那么不会用前面的遍历方法来收集元素,而是直接拿出所有元素。