做完这个就专升本了😊
选择路线: riscv32
版本:https://nju-projectn.github.io/ics-pa-gitbook/ics2022/index.html
地址:https://github.com/fennecs/ics2022 (private)
在愉快的PA之旅之前
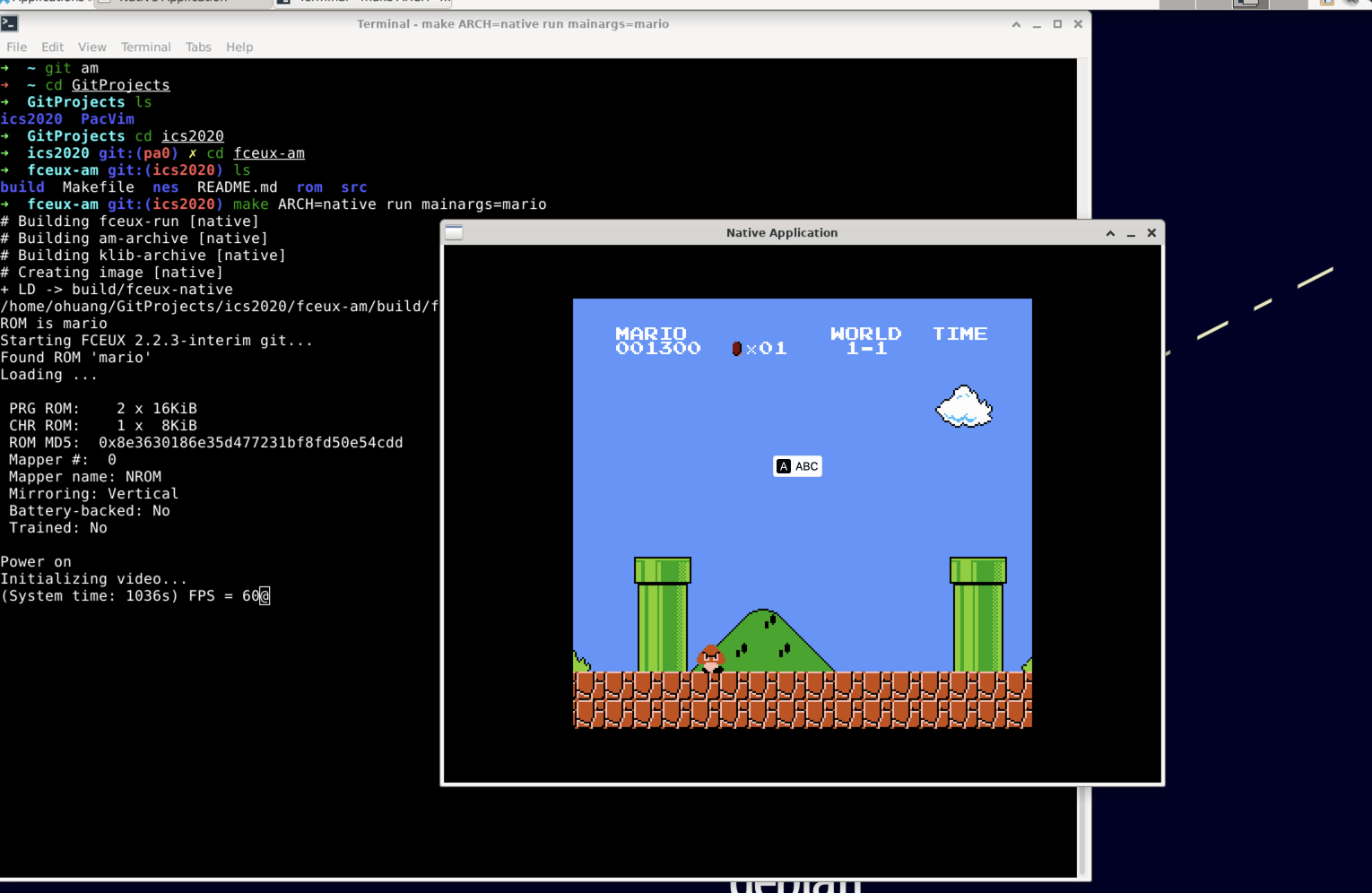
照着讲义git clone之后,一通折腾,最后执行make ARCH=native run mainargs=mario成功运行,but
...
PRG ROM: 2 x 16KiB
CHR ROM: 1 x 8KiB
ROM MD5: 0x8e3630186e35d477231bf8fd50e54cdd
Mapper #: 0
Mapper name: NROM
Mirroring: Vertical
Battery-backed: No
Trained: No
Power on
Initializing video...
卡在Initializing video...了,盲猜是没有装GUI,装上xface、xrdp、远程连接客户端,成功运行again。
不过怎么没有声音呢?虽然讲义说不是必选,可是作为一个计(^)算(C)机(V)科(工)学(程)家(师),你既然提了可以做到,我就必须得开这个声音了,远程协议用的xrdp,于是去github一波,看到README.md有这样的内容:

顺着Audio redirection的链接过去,是一个pulseaudio-module-xrdp模块,需要编译两个.so,我的是debian,编译过程一直出现
Reading package lists...
Building dependency tree...
E: Unable to locate package sudo
E: Unable to locate package lsb-release
/bin/sh: 1: cannot create /etc/sudoers.d/nopasswd-ohuang: Directory nonexistent
chmod: cannot access '/etc/sudoers.d/nopasswd-ohuang': No such file or directory
/wrapped_script: 55: lsb_release: not found
/wrapped_script: 55: lsb_release: not found
在issue里找到了解决办法,是apt源的原因,轻量云用的源是腾讯的镜像源,改为官方源就好了。
configure的时候遇到了波浪线在双引号内无法解释的问题,命令改为./bootstrap && ./configure PULSE_DIR=/home/$USER/pulseaudio.src,最后make && sudo make install即可,执行
ls $(pkg-config --variable=modlibexecdir libpulse) | grep xrdp
显示
module-xrdp-sink.la
module-xrdp-sink.so
module-xrdp-source.la
module-xrdp-source.so
重启一下服务器,可以在声音看到xrdp的字眼
再运行一波,声来!
开天辟地的篇章
计算机可以没有寄存器吗? (建议二周目思考)
可以,用内存代替,但是会很慢。实际上, 寄存器就是内存的一种缓存实现.
从状态机视角理解程序运行
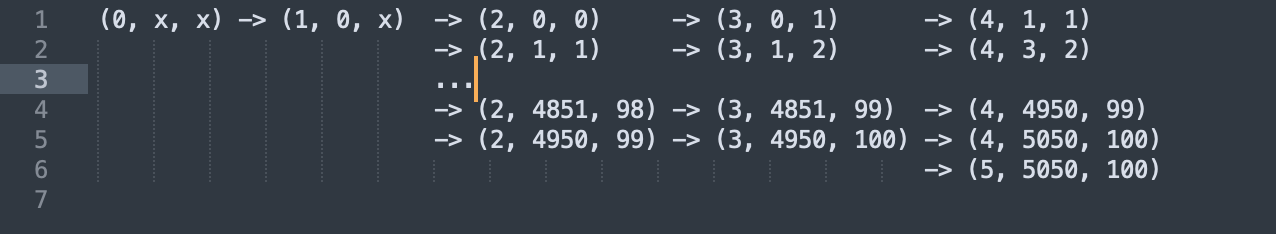
P.S. 转移指令只会引起PC寄存器变化
RTFSC
x86
执行make ISA=x86 run却跑不起来,原因是x86的cpu结构需要实现。
注释提示要使用匿名联合体,因为eax, ecx, edx, ebx, esp, ebp, esi, edi这几个字段也要共用AL等寄存器空间。
diff --git a/nemu/include/isa/x86.h b/nemu/include/isa/x86.h
index 6d4d9d8..3d140be 100644
--- a/nemu/include/isa/x86.h
+++ b/nemu/include/isa/x86.h
@@ -18,18 +18,22 @@
*/
typedef struct {
- struct {
- uint32_t _32;
- uint16_t _16;
- uint8_t _8[2];
- } gpr[8];
+ union { // 这里要匿名,匿名之后gpr和eax, ..可以作为x86_CPU_state的成员直接使用
+ union { // 这里是否匿名无所谓,因为有gpr变量作为作用域了
+ uint32_t _32;
+ uint16_t _16;
+ uint8_t _8[2];
+ } gpr[8];
/* Do NOT change the order of the GPRs' definitions. */
/* In NEMU, rtlreg_t is exactly uint32_t. This makes RTL instructions
* in PA2 able to directly access these registers.
*/
- rtlreg_t eax, ecx, edx, ebx, esp, ebp, esi, edi;
+ struct {
+ rtlreg_t eax, ecx, edx, ebx, esp, ebp, esi, edi;
+ };
+ };
vaddr_t pc;
} x86_CPU_state;
究竟要执行多久?
void cpu_exec(uint64_t n);
cpu_exec的函数声明如上,入参是一个无符号数,所以-1会转换为一个64位的正整数,这需要跑2^64条指令才能跑完这个循环。
潜在的威胁 (建议二周目思考)
The C Standard says that if a program has signed integer overflow its behavior is undefined.传送门
也就是说把负数传给无符号数是一种未定义行为,C标准是不打包票能按二进制字面量转换的(但是大部分实现都都是按二进制字面转换。
谁来指示程序的结束?
exit()函数,在任意位置发生这个调用,操作系统会收到此信号并终止进程。
程序是个状态机, 这个函数的作用就是把状态机流转到停止.
链接时crt会把main()的返回码作为exit()的入参, 发起一个syscall, 停止状态机.
有始有终 (建议二周目思考)
(TODO)
其他
Do NOT change the order of the GPRs’ definitions.
代码里寄存器的顺序和手册里的不一样,
rtlreg_t eax, ecx, edx, ebx, esp, ebp, esi, edi;
这是因为代码寄存器顺序按编码排列的
| 二进制编码 | 000 | 001 | 010 | 011 | 100 | 101 | 110 | 111 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8位寄存器 | AL | CL | DL | BL | AH | CH | DH | BH |
| 16位寄存器 | AX | CX | DX | BX | SP | BP | SI | DI |
| 32位寄存器 | EAX | ECX | EDX | EBX | ESP | EBP | ESI | EDI |
为什么要按编码排列呢,因为使用寄存器的opcode(操作码)是按寄存器的编码顺序排列的
比如MOV指令,b0~b7使用的是byte register,b8~bf是用的是32-bit register,模拟器进行寄存器寻址时只要用s->opcode & 0x7就可以取得寄存器的下标。

表达式求值
为什么printf()的输出要换行?
因为printf是C标准库,自带了一个buffer,printf标准输出只有遇到换行符才会冲刷缓冲区。
表达式生成器如何获得C程序的打印结果?
用system函数执行shell命令编译,popen可以获得一个管道,把运行的程序的标准输出,作为本程序的标准输入,fscanf解析标准输入,便得到C程序的打印结果。
如何生成长表达式, 同时不会使buf溢出?
(首先,我没有实现考虑随机插入空格,因为有点鸡肋。)
我们要保证buf不溢出,就要做好长度限制。
假设表达式的生成方式是rand() % 1000,也就是一个数字最多占3个字符。
字符串的长度是strlen(buf), 数组的可用长度是LENGTH - 1(我就是没有减1导致buf数组越界丢了\0找了好久)。
讲义把生成表达式的框架给出来了,三种case都可以生成完整的表达式,三种case所需要的cost不同,我们再加上计算remain的表达式。
根据remain讨论case
#define BUF_LENGTH 65536
static inline void gen_rand_expr() {
int remain = LENGTH - 1 - strlen(buf); // not final
switch (choose(3)) {
case 0:
gen_num();
break;
case 1:
gen('(');
gen_rand_expr();
gen(')');
break;
default: // case 2
gen_rand_expr();
gen_rand_op();
gen_rand_expr();
break;
}
}
其实这里remain的计算方式
这里用一个全局变量count记录未出栈的字符长度,这部分长度也是buf长度的一部分
于是switch代码变成
#define NUM_LENGTH 10
switch (choice) {
case 0: // cost at least NUM_LENGTH
gen_num();
break;
case 1: // cost at least NUM_LENGTH + 2
gen('('); // cost 1
count++;
gen_rand_expr();// cost NUM_LENGTH
gen(')'); // cost 1
count--;
break;
default/* 2 */: // cost at least NUM_LENGTH * 2 + 1
count += NUM_LENGTH + 1;
gen_rand_expr(); // cost NUM_LENGTH
gen_rand_op(); // cost 1
count -= NUM_LENGTH + 1;
gen_rand_expr(); // cost NUM_LENGTH
break;
}
然后remain的计算方式应该包含count
int remain = LENGTH - 1 - strlen(buf) - count;
知道了剩余空间,分析3个case需要的字符数
case0: 至少需要NUMBER_LENGTH个字符
case1: 至少需要NUMBER_LENGTH + 2个字符
case2: 至少需要NUMBER_LENGTH * 2 + 1个字符
于是有
int choice = 0;
if (remain >= NUM_LENGTH * 2 + 1) {
choice = choose(3);
} else if (remain >= NUM_LENGTH + 2) {
choice = choose(2);
} else if (remain >= NUM_LENGTH) {
choice = choose(1);
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "cannot reach here!\n");
exit(-1);
}
switch(choice) {
...
}
为什么要使用无符号类型? (建议二周目思考)
结合下面的问题,感觉和0有关,但是说不出来。
除0的确切行为
除数为0在linux下会coredump,macos会返回随机数(undefined行为)
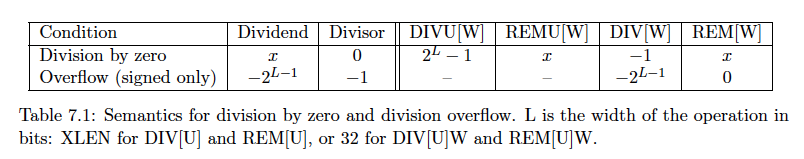
在riscv手册中,关于除以0的说法如下:
The semantics for division by zero and division overflow are summarized in Table 7.1. The quotient of division by zero has all bits set, and the remainder of division by zero equals the dividend. Signed division overflow occurs only when the most-negative integer is divided by -1. The quotient of a signed division with overflow is equal to the dividend, and the remainder is zero. Unsigned division overflow cannot occur.
过滤除0行为的表达式
fscanf可以返回parse成功个数,而除以0在linux下会导致coredump,这种情况下我们生成测试用例的code在stdout是没有输出的,fscanf会返回-1,所以可以根据这个行为过滤。
监视点
温故而知新
static是静态变量,加在全局变量上可以保证声明只局限于此文件。(其实就是把全局变量私有,防止别的代码直接修改,这个是和java不一样的。
你会如何测试你的监视点实现?
单步运行,使用默认image,当寄存器值变化的时候,程序是否按预期停下来。
强大的GDB
可以用bt命令看到现场堆栈,通过f命令跳转栈帧,通过p命令打印现场参数
如何提高断点的效率 (建议二周目思考)
NEMU的断点机制是每个指令都要check一遍,这无疑至少执行了两倍指令,现在cpu都会提供用于debug的指令,比如x86的int3,这是一个单字节指令。当gdb打断点的时候会把代码行对应的pc的指令替换为int3,程序会和普通程序一样执行,但是跑到int3指令的时候,会陷入内核进入阻塞,产生中断编号为3的中断。
一点也不能长?
断点的本质是替换程序的二进制,如果指令多于一个字节,可能会有其他线程跳到第二个被替换的指令的位置,会发生什么咱也不知道。
随心所欲的断点
这是未定义行为,大部分指令一上来就是opcode了,如果int3嵌到指令中间部分,可能会被解释为操作数或者寄存器,所以这是不行的。
NEMU的前世今生
具体看看这个
如何阅读手册
必答题
x86
- CF: Carry Flag,(人称穿越火线(误)),用于存储进位。See 3.8 Flag Control Instructions
- ModR/M: A byte, known as the modR/M byte, follows the opcode and specifies whether the operand is in a register or in memory。即用一个额外的字节实现复杂的操作数,See17.2 Instruction Format
- MOV: intel指令格式是
MOV <to> <from>. See MOV – Move Data
riscv32
- 6种
R(r2r),I(i2r),S,B,U,J(其中SB,UJ只是立即数的编码不同),一看就比x86的简单n倍 - LUI (load upper immediate) is used to build 32-bit constants and uses the U-type format. LUI places the U-immediate value in the top 20 bits of the destination register rd, filling in the lowest 12 bits with zeros.
Immediate Encoding Variants
S和B,U和J是同一种指令,只是后者立即数范围更大。可以看到立即数的bit排列不是顺序的,官方文档说:
Although more complex implementations might have separate adders for branch and jump calculations and so would not bene t from keeping the location of immediate bits constant across types of instruction, we wanted to reduce the hardware cost of the simplest implementations. By rotating bits in the instruction encoding of B and J immediates instead of using dynamic hardware muxes to multiply the immediate by 2, we reduce instruction signal fanout and immediate mux costs by around a factor of 2. The scrambled immediate encoding will add negligible time to static or ahead-of-time compilation. For dynamic generation of instructions, there is some small additional overhead, but the most common short forward branches have straightforward immediate encodings.
大致意思就是保证bit位置不变能提高速度。
结尾
PA1结束,进入PA2